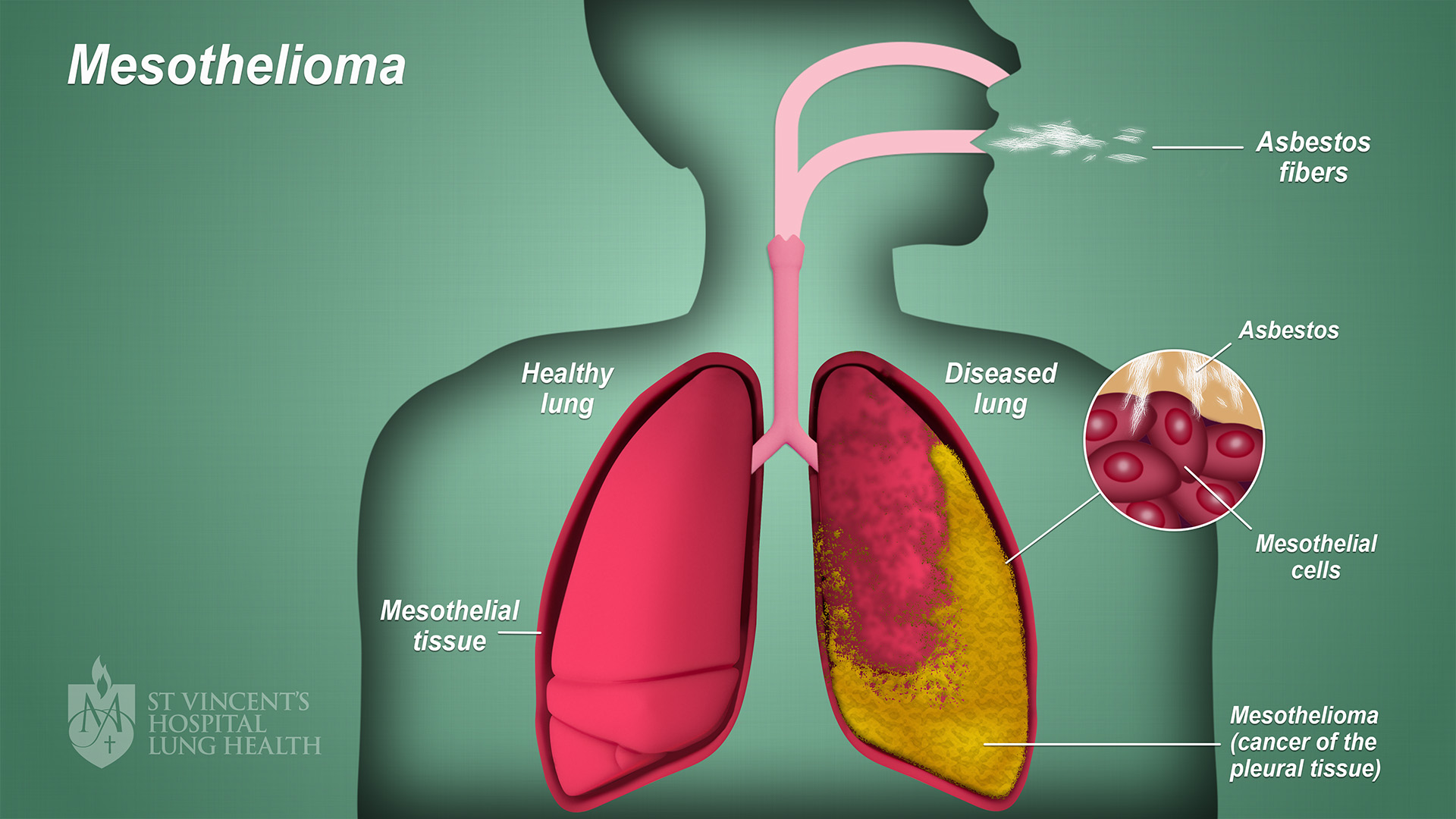
Introduction
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer, typically caused by prolonged exposure to asbestos. Due to its long latency period, diagnosis often occurs at an advanced stage, making survival rates a key concern for patients and their families. While survival rates offer general guidance, many factors influence a patient’s outlook. In this article, we’ll explore mesothelioma survival rates, the variables that impact them, and steps patients can take to improve their chances of extending life expectancy.
What Are Mesothelioma Survival Rates?
Survival rates indicate the percentage of patients who live for a specified period after their diagnosis. For mesothelioma, survival is generally measured in one-, three-, and five-year intervals.
- One-Year Survival Rate: Around 40% of mesothelioma patients live one year or longer after diagnosis.
- Three-Year Survival Rate: Approximately 10-20% of patients survive for three years.
- Five-Year Survival Rate: Only about 5-10% of mesothelioma patients live beyond five years.
However, these statistics are broad averages and may vary depending on multiple factors.
Factors Affecting Mesothelioma Survival Rates
Mesothelioma survival rates are influenced by a range of variables, including the stage of cancer at diagnosis, patient demographics, and the type of mesothelioma. Below are some key factors:
1. Stage of Mesothelioma
One of the most significant determinants of survival is the stage at which mesothelioma is diagnosed.
- Early Stage (Stage I or II): If diagnosed early, patients have better treatment options, such as surgery, that can remove tumors and improve survival. The one-year survival rate for early-stage patients is higher, often above 50%.
- Advanced Stage (Stage III or IV): In advanced stages, the cancer has spread beyond the lining of the lungs or abdomen, making it more challenging to treat. For patients diagnosed at this stage, the one-year survival rate drops significantly, often to around 30%.
2. Type of Mesothelioma

There are four main types of mesothelioma, each affecting survival rates differently:
- Pleural Mesothelioma: The most common type, affecting the lungs, pleural mesothelioma has an average survival of about 12-18 months.
- Peritoneal Mesothelioma: This affects the abdomen and generally has a better prognosis. Patients who undergo cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) may have a survival rate of 3-5 years or longer.
- Pericardial Mesothelioma: Affecting the heart, pericardial mesothelioma is extremely rare and usually has a very poor prognosis, with most patients living less than a year.
- Testicular Mesothelioma: The rarest form of the disease, testicular mesothelioma often responds better to treatment, and patients may live for several years after diagnosis.
3. Age and Overall Health
Younger patients, particularly those under 50, generally have better survival rates than older patients. A strong immune system, absence of other chronic diseases, and overall physical fitness allow younger individuals to better withstand aggressive treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Younger Patients: Typically have a five-year survival rate closer to 10-20%.
- Older Patients (Over 65): The five-year survival rate drops significantly, often below 5%, due to age-related health complications and reduced ability to handle intensive treatments.
4. Treatment Options
The types of treatments available to a patient have a significant impact on survival rates. Patients with access to specialized mesothelioma treatments often have improved outcomes.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention can significantly improve survival, especially if done at an early stage. For instance, pleurectomy/decortication (P/D) and extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP) can extend life expectancy.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: These treatments are commonly used, either alone or in combination, to control cancer growth and alleviate symptoms. Chemotherapy can increase one-year survival rates to nearly 50%.
- Clinical Trials: Patients who participate in clinical trials may have access to cutting-edge therapies such as immunotherapy, which is showing promising results in extending survival rates.
5. Gender
Surprisingly, gender plays a role in mesothelioma survival rates. Studies suggest that women tend to have better survival outcomes than men. Some research suggests that this may be due to hormonal differences or variations in how men and women respond to treatment.
- Female Patients: Women with pleural mesothelioma have a median survival rate of 22.2 months.
- Male Patients: Men typically have a shorter median survival, around 16.3 months.
Ways to Improve Mesothelioma Survival Rates
Although mesothelioma is often considered a terminal diagnosis, there are several steps patients can take to improve their chances of survival.
1. Early Diagnosis
Early detection is critical for improving survival rates. Patients exposed to asbestos should regularly monitor their health, reporting any signs of respiratory issues to a doctor. Diagnostic tools like CT scans and MRIs can help detect mesothelioma at an earlier, more treatable stage.
2. Seeking Specialized Care
Finding a mesothelioma specialist is key to accessing advanced treatment options. These specialists are more likely to offer innovative treatments, such as immunotherapy or surgery combined with HIPEC, that may extend life expectancy.
3. Participating in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials offer patients access to emerging therapies that are not widely available. These experimental treatments, such as targeted therapy or gene therapy, may provide better outcomes than traditional treatments.
Conclusion
Mesothelioma survival rates are influenced by a range of factors, including the stage of diagnosis, type of mesothelioma, treatment options, and the patient’s overall health. Although the survival outlook for mesothelioma patients can seem daunting, advances in treatment and early detection efforts are helping to improve survival outcomes. By seeking specialized care, participating in clinical trials, and maintaining overall health, patients can improve their chances of beating the odds.